Smoke Testing is a kind of software testing process that confirms the testers and software team as to whether to proceed with the further testing process or not. It includes a minimal number of test cases to be run on software to test main functionalities. In layman's terms, the tester verifies whether the critical and main features are working and there are no showstoppers in the build that is under testing by the testing team.
It is a small and quick regression test of major functionality. It is a simple test that depicts the software as ready for testing. This helps a testing team to determine if the build is flawed to make any further testing a waste of time and resources.
Why Smoke Testing?
Smoke testing plays a vital role in the software development cycle as it verifies the correctness of the software system in the very initial stages. By this, the developers and the testers will come to know the earlier defects. Once smoke testing is completed and is passed then the testers can continue the further testing.
How to do Smoke Testing for a Software?
Once the build is released or code is deployed for QA, high-priority and major functionality test cases are considered and tested to identify the critical bugs in the system. Smoke testing is carried out once a new build is released. One thing Testers need to keep in mind is that before performing smoke testing, one should always ensure that testing is carried out on the correct build version.
Smoke Testing Cycle:
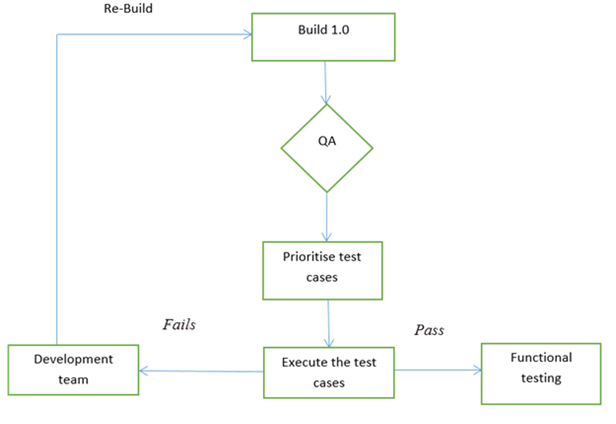
Regression Testing:
In simple words, Regression Testing is a kind of testing that is performed to ensure that the recent changes in the software haven’t hampered the existing features in the software. Regression testing can be defined as a kind of software testing to verify that a recent program or code change has not affected existing features of the software.
Regression Testing is a full or partial selection of already executed test cases that are re-executed to verify existing functionalities are working fine. This kind of testing is conducted to ensure that changes in new code should not have side effects on the existing functionalities.
Why Regression Testing?
Regression testing is carried out mainly when there is a requirement to alter the code and when testers need to test whether the modified code has affected the existing part of the code or not. Additionally, it is required when a new feature is added to the software and to check, the defect fixes as well as for verifying performance issue fixes.
How to do Regression Testing for a Software Application?
To carry out Regression Testing, the testers need to select the test cases from the test suite that already exists that covers both modified and affected areas of the code of the software.
Software maintenance is such a kind of activity that includes enhancement of the same, defect fixing, optimization, and deletion of existing features in the same application. These changes may cause the software as a whole to work incorrectly (not as per expectations). Therefore, Regression Testing becomes one of the important parts of testing. Regression Testing can be performed using the following techniques:
1) Retest All
In this kind of regression technique, all the test cases are re-executed.
2) Regression Test Selection
Few selected test cases are re-run to ensure the stability of existing features due to newly implemented code. Test cases are divided into 2 parts:
a) Re-usable test cases: which can be used in further regression cycles.
b) Obsolete Test cases: which cannot be used in succeeding regression cycles.
3) Prioritization of Test cases
Prioritizing test cases purely depends upon the criticality and frequency of usability of functionalities.
Challenges in Regression Testing:
With more regression cycles, the test suite becomes larger. Time and budget
- Constraints make up the entire execution of the regression test suite.
- There is always a challenge to maximize test coverage while minimizing the test suite.
- Determining the frequency of Regression Tests for software.