What are Locators?
Locators are strategies used to identify and locate specific web elements within the HTML structure of a web page, also known as the Document Object Model (DOM). Selenium WebDriver uses these locator strategies to find elements like buttons, text fields, or links and perform actions such as clicking, typing, or validating during test automation.
How to pick Locators?
To pick a locator of an element, open the web application on your browser. Do right click > Inspect or Press F12 directly on your keyboard, it will open DevTools of the browser. In DevTools > Elements Tab, you can see the DOM of the page, which is raw HTML.
To locate a web element using Selenium WebDriver, follow these steps:
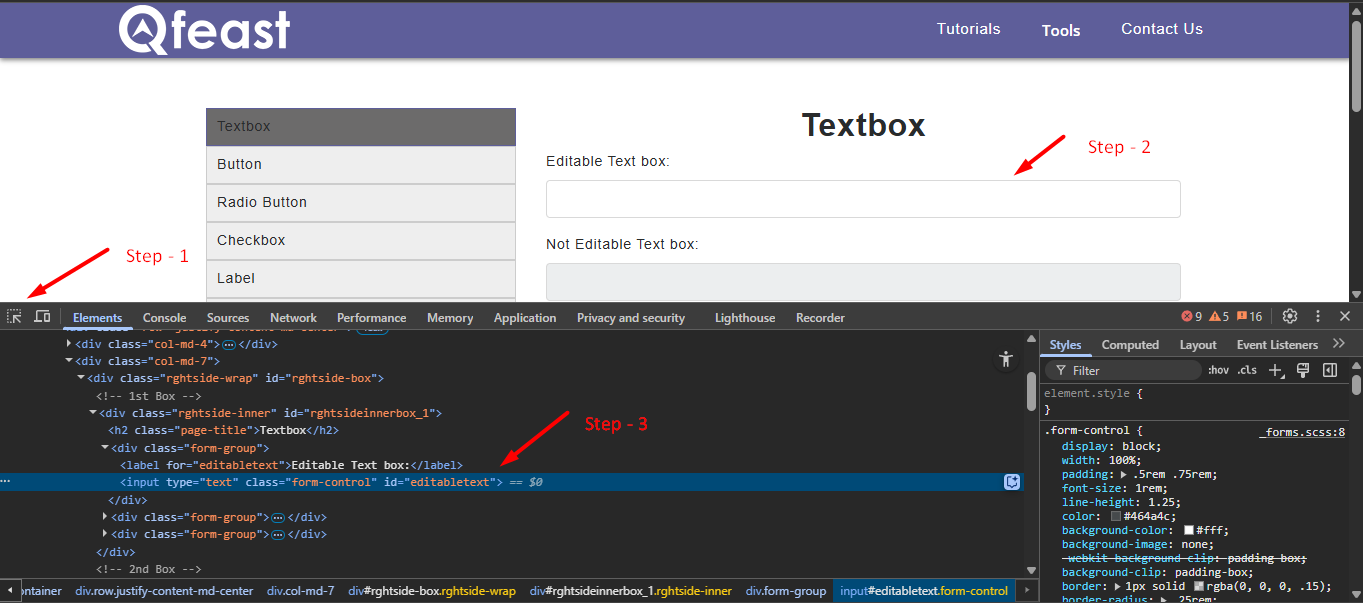
Step 1: Click the Select element icon in Chrome DevTools.
Step 2: Hover over and click the element on the web page that you want to inspect.
Step 3: The corresponding HTML code will be highlighted in the Elements tab.
You can then identify useful attributes like id, class, or name to choose the best locator strategy.
Types of Locators in Selenium WebDriver
Selenium WebDriver provides different types of locators to identify elements efficiently based on their HTML attributes or structure. Each locator targets specific properties such as id, name, class, or even XPath and CSS selectors.
Before exploring the types of locators, it is important to understand two key methods used to find elements in Selenium Java.
findElement(): This method locates the first matching web element on the page and returns it. If no element is found, it throws a NoSuchElementException.
findElements(): This method locates all matching elements and returns them as a list. If no elements are found, it returns an empty list.
Example Syntax:
Here are some of the common Locator types in Selenium WebDriver
|
Locator Type |
Syntax Example |
When to Use |
|
ID |
driver.findElement(By.id("idValue")) |
Most reliable if ID is unique |
|
Name |
driver.findElement(By.name("nameValue")) |
When ID is not available, but Name is unique |
|
Class Name |
driver.findElement(By.className("className")) |
When a Class is unique |
|
CSS Selector |
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("input#username")) |
Very fast and flexible |
|
XPath |
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//tag[@attribute='value']")) |
Powerful but slower, use when no other option |
|
Link Text |
driver.findElement(By.linkText("Full Link Text")) |
Clicking on an exact link text |
|
Tag Name |
driver.findElement(By.tagName("input")) |
Working with multiple similar elements |
|
Partial Link Text |
driver.findElement(By.partialLinkText("Partial Text")) |
Clicking using partial link text |
How to Pick the Right Locator
Picking the right locator is key to making your Selenium tests reliable, fast, and maintainable. While picking locators, we need to make sure that the locator will be stable and perform better than others. Here is the order to pick the locator.
1. ID: Fastest and most reliable element.
2. Name: Pick if id is not available and the name is unique.
3. Class Name: Many elements share class names, check that the class is unique.
4. CSS Selector: Powerful and flexible. Often used when id or name is not available.
5. Xpath: Very Powerful, but slower and more brittle if the DOM Changes.
6. Link Text/Partial Link Text: Use while interacting with links based on visible text.
Always prefer unique and static attributes like id, name. Avoid auto-generated or dynamic attributes while selecting locators.